MEDICAL IMAGE REGISTRATION
Reliable and performant compensation of patient movements between different image acquisitions and modalities.
Our Medical Image Registration Features
With Chimaera's Medical Image Registration, it becomes possible to compensate for misalignment up to and including complex patient movements between different image acquisitions, whether for follow-up images, stitching of images, or acquisitions with different imaging modalities such as CT, MR or PET/SPECT.
Provided as an OEM component with C-API, our Image Registration is perfect for extending existing customer applications with additional features that require accurate spatial mapping.
Rigid Registration
Rotation and translation only
Image content is not modified
No manual parameterization needed
2D, 3D, and time series
Supports multi-modal data (e.g. CT, MR, PET, SPECT, etc)
Nonrigid Registration
Computes complex deformations between images
Deformation field can compensate for respiratory motion, cardiac motion, patient positioning, etc
Easy and flexible parameterization for different use cases
2D, 3D, and time series
Supports multi-modal data (CT, MR, PET, SPECT, etc)
Medical
Image Registration –
Applications
Retrospective image fusion
Follow-up studys
Difference and perfusion imaging
4-D motion correction
Model / atlas-to-image registration
Post market surveillance
Solutions
Rigid image registration
Nonrigid image registration
Support of 2-D & 3-D image data
Benefits
Simple integration (C-API)
Low hardware requirements (CPU based)
Fully automatic rigid registration
No / minimal parameterisation (nonrigid)
Quality documents for product integration
Applications for Medical Image Registration
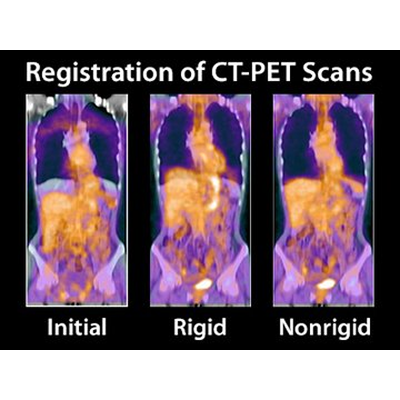
Rigid Registration
The transformation between the images is limited to only rotations and translations. This method is often used to establish a link between different scanner coordinate systems or to account for rigid body movements while the image content does not change:
Retrospective image fusion (e.g. for PET/CT, PET/MR, etc)
Side-by-side viewing of follow-up studies
Image stitching
Nonrigid Registration
Nonrigid (also sometimes denoted as deformable or elastic) image registration techniques allow far more degrees of freedom in terms of deformation compared to rigid registration. Complex deformations between images often need to be calculated to compensate for respiratory motion, cardiac motion, slight differences in patient positioning, or other types of soft tissue misalignments. Cross-patient registration is also possible to create atlases on different subjects.
Perfusion imaging
Difference imaging
Atlas registration
Transfer findings to follow-up study
In the following use case, we demonstrate how nonrigid image registration can compensate complex organ movement between a non-contrasted and an arterial phase of an MR perfusion image study.
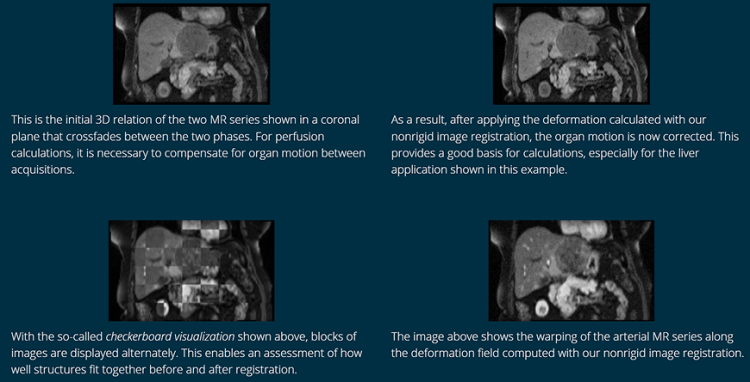
Can non-rigid image registration compensate for respiratory motion?
Yes, this is achieved by calculating a compensation transformation (deformation field) that corrects the deformations in the thorax area caused by breathing motion.
Is the Image Registration suitable for atlas creation and application?
With our non-rigid image registration, images from different patients can be combined to create an atlas. In addition, new images can be registered with the atlas. One application for this is, for example, the transfer of a segmentation atlas (brain atlas).
Can Image Registration also be used for industrial applications?
Of course, our Image Registration can be used for both 2D and 3D applications in an industrial environment, e.g. for position corrections of workpieces, for camera stitching or for calibration applications.
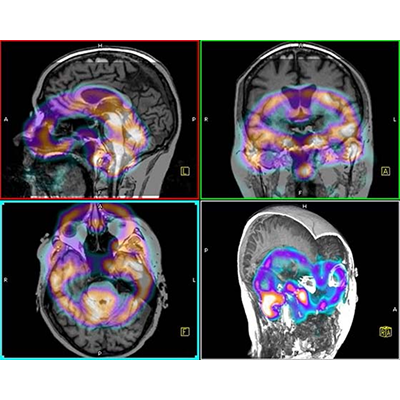
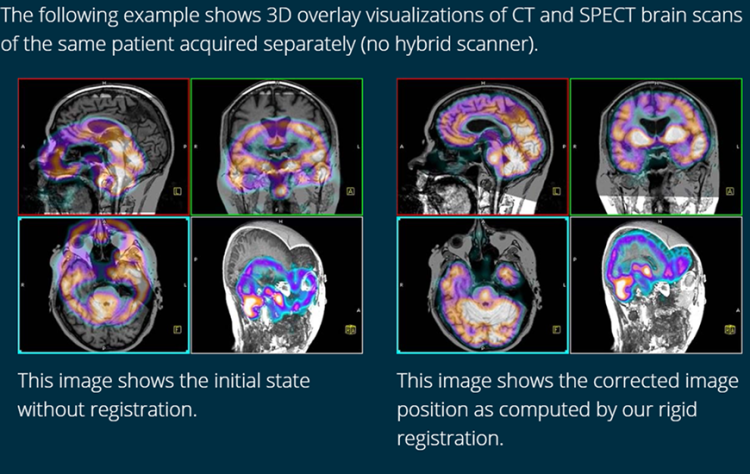
Use Cases for Medical Image Registration
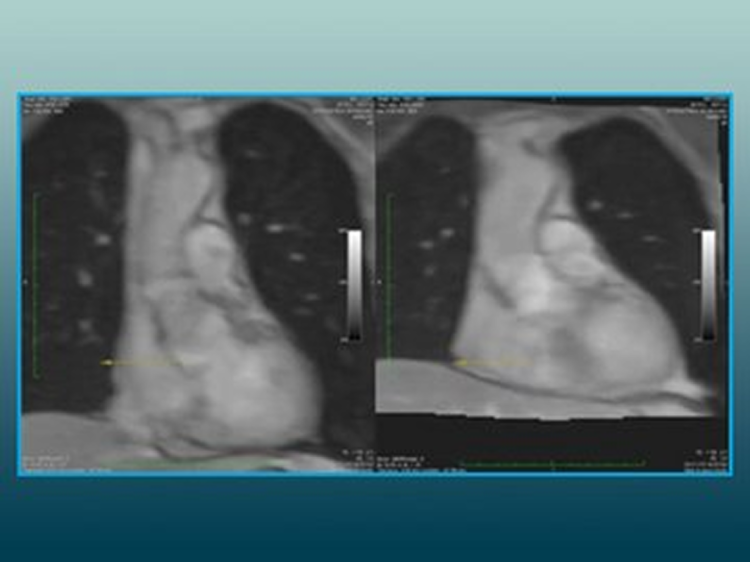
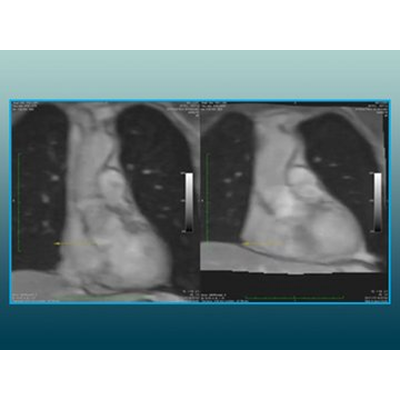
Compensation of Cardiac Motion in 3D MR Time Series
01/24/2024 Use CaseThis use case demonstrates the compensation of cardiac motion in a 3D time series acquired with an MR scanner.
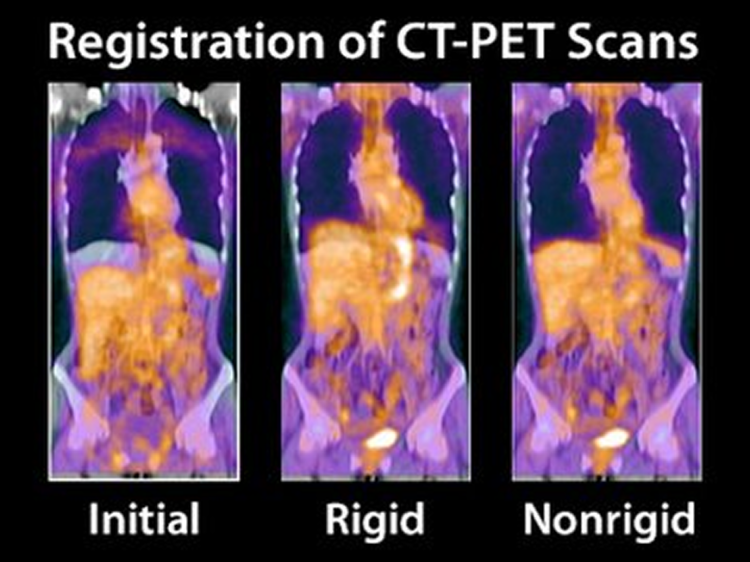
Registration of Melanoma Patient Scans
11/16/2021 Use CaseShowcase for our Image Registration to compensate respiratory motion in a PET-CT image pair of a melanoma patient. The images were acquired at different times with individual scanners.

非常抱歉,您只有购买软件后才能查看完整软件教程!